Appearance
要解决这个缺陷,就要使用到新的技巧,Few-Shot Chain of Thought。
根据 Wei 他们团队在 2022 年的研究表明:
通过向大语言模型展示一些少量的样例,并在样例中解释推理过程,大语言模型在回答提示时也会显示推理过程。这种推理的解释往往会引导出更准确的结果。
下面是论文里的案例,使用方法很简单,在技巧 2 的基础上,再将逻辑过程告知给模型即可。从下面这个案例里,你可以看到加入解释后,输出的结果就正确了。
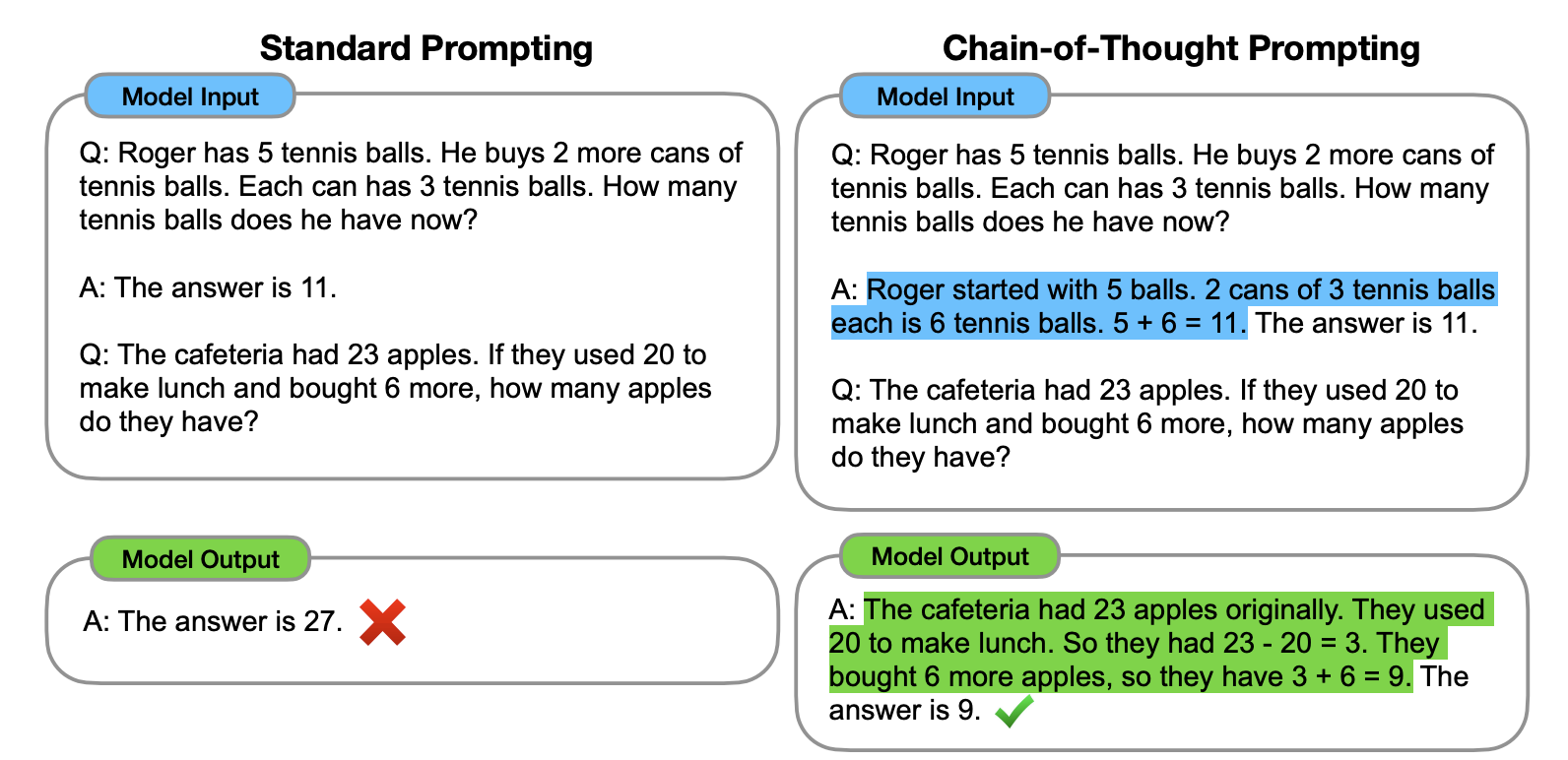
那本章开头提的例子就应该是这样的(注:本例子同样来自 Wei 团队论文):
txt
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 4, 8, 9, 15, 12, 2, 1.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (9, 15, 1) gives 25. The answer is False.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 17, 10, 19, 4, 8, 12, 24.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (17, 19) gives 36. The answer is True.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 16, 11, 14, 4, 8, 13, 24.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (11, 13) gives 24. The answer is True.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 17, 9, 10, 12, 13, 4, 2.
A: Adding all the odd numbers (17, 9, 13) gives 39. The answer is False.
The odd numbers in this group add up to an even number: 15, 32, 5, 13, 82, 7, 1.
A:聊完技巧,我们再结合前面的 Zero-Shot Chain of Thought,来聊聊 Chain of Thought 的关键知识。根据 Sewon Min 等人在 2022 年的研究 表明,思维链有以下特点:
- "the label space and the distribution of the input text specified by the demonstrations are both key (regardless of whether the labels are correct for individual inputs)" 标签空间和输入文本的分布都是关键因素(无论这些标签是否正确)。
- the format you use also plays a key role in performance, even if you just use random labels, this is much better than no labels at all. 即使只是使用随机标签,使用适当的格式也能提高性能。
理解起来有点难,我一个 prompt 案例给大家解释(🆘 如果你有更好的解释,不妨反馈给我)。我给 ChatAI 一些不一定准确的例子:
txt
I loved the new Batman movie! // Negative
This is bad // Positive
This is good // Negative
What a good show! //Output 是这样的:
txt
Positive在上述的案例里,每一行,我都写了一句话和一个情感词,并用 // 分开,但我给这些句子都标记了错误的答案,比如第一句其实应该是 Positive 才对。但:
- 即使我给内容打的标签是错误的(比如第一句话,其实应该是 Positive),对于模型来说,它仍然会知道需要输出什么东西。换句话说,模型知道 // 划线后要输出一个衡量该句子表达何种感情的词(Positive or Negative)。这就是前面论文里 #1 提到的,即使我给的标签是错误的,或者换句话说,是否基于事实,并不重要。标签和输入的文本,以及格式才是关键因素。
- 只要给了示例,即使随机的标签,对于模型生成结果来说,都是有帮助的。这就是前面论文里 #2 提到的内容。
最后,需要记住,思维链仅在使用大于等于 100B 参数的模型时,才会生效。
BTW,如果你想要了解更多相关信息,可以看看斯坦福大学的讲义:Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning